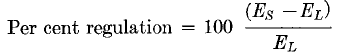| Electronic Transformers and Circuits is a free introductory textbook on transformers and related circuits. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Introduction Introduction  Regulation, Efficiency, and Power Factor Regulation, Efficiency, and Power Factor |
|||||||||||






|
|||||||||||
Regulation, Efficiency, and Power Factor
Transformer regulation is the difference in the secondary terminal voltage at full load and at no load, expressed as a percentage of the full-load voltage. For the resistive load of Fig. 3(a), (b), and (c),
Since with low values of leakage reactance Es - EL = IR,
provided that R includes the primary winding resistance multiplied by the factor (N2/N1)2 as well as the secondary winding resistance. If leakage reactance is not negligibly small, approximately
Efficiency is the ratio
where losses include both core and winding losses. A convenient way of expressing power factor is
Equation 16 gives the power factor of a transformer plus its load. One of the problems of transformer design is the proper choice of induction to obtain low values of exciting current and high power factor. Low power factor may cause excessive primary winding copper loss, low efficiency, and overheating.
|
|||||||||||
Home  Introduction Introduction  Regulation, Efficiency, and Power Factor Regulation, Efficiency, and Power Factor |
|||||||||||
Last Update: 2011-01-24