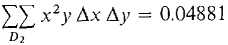| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Multiple Integrals Multiple Integrals  Double Integrals Double Integrals  Examples Examples  Example 2 Example 2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Example 2
Find the double Riemann sum
where D2 is the region 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, x2 ≤ y ≤ √x and Δx = ¼ Δy = 1/5.
Figure 12.1.11 The circumscribed rectangle of D2 is the unit square. The partition and D2 are shown in Figure 12.1.11 and the partition points which actually belong to D2 are circled. The table shows the values of x2y at the partition points which belong to D2. It is a part of the table from Example 1.
The double Riemann sum is
= A similar computation with Δx = 1/10, Δy = 1/10 gives
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Home  Multiple Integrals Multiple Integrals  Double Integrals Double Integrals  Examples Examples  Example 2 Example 2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Last Update: 2010-11-25


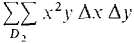

 =
=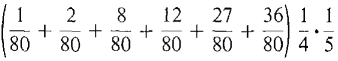 =
= 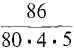 = 0.05375.
= 0.05375.