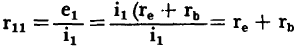| Transistor Basics is a free introductory textbook on transistors and their basic applications. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Grounded Emitter and Grounded Collector Transistors Grounded Emitter and Grounded Collector Transistors  The Grounded Emitter Connection The Grounded Emitter Connection  Circuit Parameters Circuit Parameters |
||||||||||||||






|
||||||||||||||
|
Circuit ParametersAuthor: Leonard Krugman
These grounded-emitter relationships are derived as follows: A.
B.
C.
D. Using the same equations as in C above, when i1 = 0, e2 = i2 (re + rc - rm) then The open-circuit characteristics can now be numerically evaluated for the typical point-contact and junction transistors previously considered in Chapter 3. For the point-contact transistor in the grounded emitter connection:
For the junction transistor in the grounded emitter connection:
Because of the large values of rm and rc with respect to re, r21 in the practical case can be approximated by -rm, and r22 by (rc - rm). The emitter resistance, re = r12, is the feedback resistance and is equivalent to rb = r12 in the grounded base connection. Notice, however, that since there is phase inversion in the grounded emitter connection, re produces degenerative (negative) feedback, rather than regenerative (positive) feedback. The degenerative effect of the output current through re is similar to the degenerative action of an unbypassed cathode resistor in a grounded cathode vacuum tube.
|
||||||||||||||
Home  Grounded Emitter and Grounded Collector Transistors Grounded Emitter and Grounded Collector Transistors  The Grounded Emitter Connection The Grounded Emitter Connection  Circuit Parameters Circuit Parameters |
||||||||||||||
Last Update: 2010-11-17