| Radio Antenna Engineering is a free introductory textbook on radio antennas and their applications. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  High-frequency Antennas High-frequency Antennas  Simple Directive High-frequency Antennas Simple Directive High-frequency Antennas  Horizontal Dipole with Parasitic Elements Horizontal Dipole with Parasitic Elements |
||||||||






|
||||||||
|
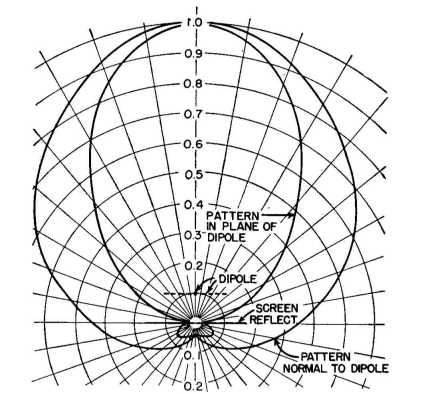
Horizontal Dipole with Parasitic ElementsAuthor: Edmund A. Laport This type of array is composed of two parallel horizontal dipoles, one of which is fed and the other is self-resonant and excited by the field of the radiator.
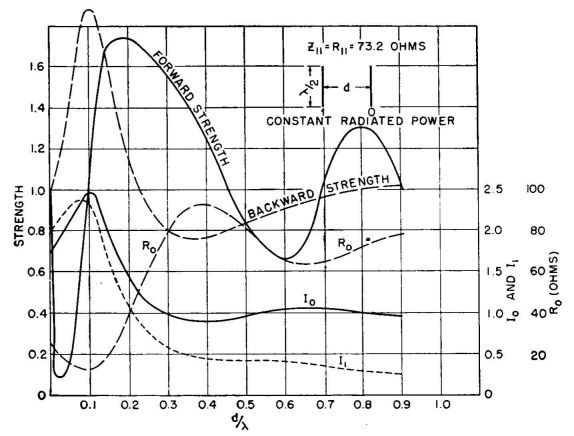
With changes in height it is possible to make small adjustments to maintain a maximum field strength on the beam. A gain of 4 to 6 decibels is available in the arrangement shown in Fig. 3.34. Using rigid members and operating at a sufficiently high frequency, this array can be mounted on one support, which can be rotated to any azimuth. The pattern can be inverted and the director changed to a reflector by tuning the parasitic element off self-resonance on the side that will give it a positive reactance. This can be done by inserting inductance at the center or by adjusting the length of the parasitic element. Figure 3.35 shows the relations between two radiation-coupled dipoles in free space when their lengths are such as to have zero self-reactance.
|
||||||||
Home  High-frequency Antennas High-frequency Antennas  Simple Directive High-frequency Antennas Simple Directive High-frequency Antennas  Horizontal Dipole with Parasitic Elements Horizontal Dipole with Parasitic Elements |
||||||||
Last Update: 2011-03-19