| The Compendium Geometry is an eBook providing facts, formulas and explanations about geometry. |

|

Home  Coordinate Systems Coordinate Systems  3D 3D  Cartesian Coordinate System Cartesian Coordinate System |
|||
| See also: 2D Cartesian Coordinate System, Conversion between 3D Coordinate Systems, Cylindrical Coordinate System, Spherical Coordinate System | |||






|
|||
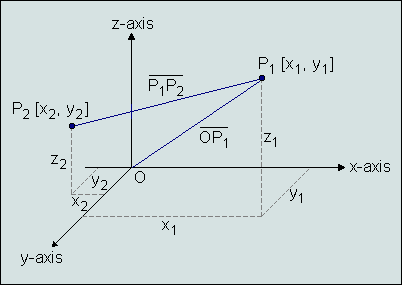
Three-dimensional Cartesian Coordinate SystemThe three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate is defined by three axes at right angles to each other, forming a three dimensional space. The three axes are labeled x (sometimes called abscissa), y (ordinate), and z (applicate). The point of intersection, where the axes meet, is called the origin, which is normally labeled O. To specify a particular point on a three dimensional coordinate system, you indicate the particular values on the axes in the form [x,y,z].
The distance between a point P and the origin O calculates from the Pythagorean theorem:
|
|||
Home  Coordinate Systems Coordinate Systems  3D 3D  Cartesian Coordinate System Cartesian Coordinate System |
|||
Last Update: 2010-12-06