| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Vector Calculus Vector Calculus  Theorems of Stokes and Gauss Theorems of Stokes and Gauss  Problems Problems |
|






|
|
Problems
In Problems 1-6, find the curl and divergence of the vector field.
7 Prove that for every vector field F(x, y, z) with continuous second partials, div(curl F) = 0. 8 Given a function f(x, y, z) with continuous second partials, show that
9 Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate the surface integral 10 Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate the line integral
where S is the portion of the plane z = 2x + 5y inside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 1 oriented with the top side positive. 11 Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate the line integral
where S is the portion of the plane z = px + qy + r over a region D of area A, oriented with the top side positive. 12 Use Stokes' Theorem to show that the line integral
for any oriented surface S. 13 Use Gauss' Theorem to compute the surface integral
where E is the rectangular box 0 ≤ x ≤ a, 0 ≤ y ≤ b, 0 ≤ z ≤ c. 14 Use Gauss' Theorem to compute the surface integral
where E is the rectangular box 0 ≤ x ≤ 1l, 0 ≤ y ≤ 1, 0 ≤ z ≤ 1. 15 Use Gauss' Theorem to evaluate
where E is the region 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, 0 ≤ y ≤ x, 0 ≤ z ≤ x + y. 16 Use Gauss' Theorem to evaluate
where E is the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 ≤ 4. 17 Use Gauss' Theorem to evaluate
where E is the hemisphere 0 ≤ z ≤ √(l - x2 - y2). 18 Use Gauss' Theorem to evaluate
where S is the cylinder x2 + y2 ≤ 1, 0 ≤ z ≤ 4. 19 Use Gauss' Theorem to evaluate
where E is the part of the cone
|
|
Home  Vector Calculus Vector Calculus  Theorems of Stokes and Gauss Theorems of Stokes and Gauss  Problems Problems |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-25



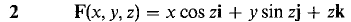





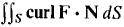 where S is the portion of the paraboloid z = 1 - x2 - y2 above the (x, y) plane and
where S is the portion of the paraboloid z = 1 - x2 - y2 above the (x, y) plane and 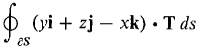
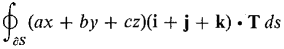
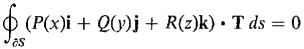


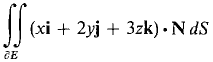
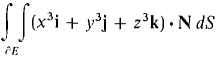

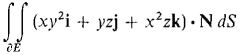
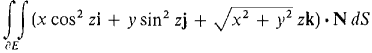
 above the (x, y) plane.
above the (x, y) plane.