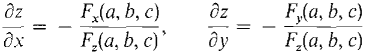| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Partial Differentiation Partial Differentiation  Implicit Functions Implicit Functions  Implicit Surface Implicit Surface |
|||||






|
|||||
Implicit Surface
Let us next consider the case where w depends on x, y, and z, while z depends on x and y, w = F(x, y, z), z = g(x, y). Figure 11.6.8 shows which variables depend on which.
Figure 11.6.8 If F(x, y, z) is smooth and ∂z/∂x, ∂z/∂y exist, the Chain Rule gives
or
Similarly,
We used the fact that for the independent variables x and y,
Notice that in this case ∂w/∂x alone is ambiguous so we had to use the more complete notation
THEOREM Suppose the function w = F(x, y, z) is smooth at the point (a, b, c), and Fz(a, b, c) ≠ 0. Then the implicit surface F(x, y, z) = 0 has the partial derivatives
and the tangent plane Fx(a, b, c)(x - a) + Fy(a, b, c)(y - b) + Fz(a, b, c)(z - c) = 0. The equation for the tangent plane is obtained as follows.
and finally Fx(a, b, c)(x - a) + Fy(a, b, c)(y - b) + Fz(a, b, c)(z - c) = 0.
|
|||||
Home  Partial Differentiation Partial Differentiation  Implicit Functions Implicit Functions  Implicit Surface Implicit Surface |
|||||
Last Update: 2006-11-25




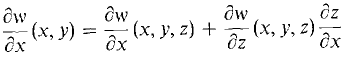

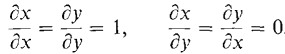
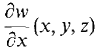 for Fx(x, y, z),
for Fx(x, y, z), for fx(x, y), where f(x, y) = F(x, y, g(x, y)).
for fx(x, y), where f(x, y) = F(x, y, g(x, y)).