| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Infinite Series Infinite Series  Absolute and Conditional Convergence Absolute and Conditional Convergence  Summary of Series Convergence Tests Summary of Series Convergence Tests |
|






|
|
Summary of Series Convergence Tests
SUMMARY OF SERIES CONVERGENCE TESTS A. Particular Series (1) Geometric Series
converges to
if |c| < 1, diverges if |c| ≥ 1. (2) Harmonic Series
(3) p Series
B. Tests for Positive and Alternating Series In the tests below, assume an ≥ 0 for all n. (1) Convergence versus Divergence to ∞ Let H be infinite.
diverges to ∞ if (2) Comparison Test Suppose an ≤ cbn for all n. If If Hint: Often a series can be compared with one of the particular series above: a geometric, harmonic, or p series. (3) Limit Comparison Test Suppose aK ≤ cbK for all infinite K. If If Hint: Try this test if the Comparison Test almost works. (4) Integral Test Suppose f is continuous, decreasing, and positive for x ≥ 1. If If Hint: This test may be useful if an comes from a continuous function f(x). (5) Alternating Series Test
C. Tests for General Series (1) Definition of Convergence
(2) Cauchy Convergence Test
diverges if for some infinite H and K > H, aH+1 + ... + aK Hint: This test is useful for showing a series diverges. (3) Constant and Sum Rules Sums and constant multiples of convergent series converge. (4) Tail Rule
(5) Absolute Convergence If Hint: Remember that Thus tests in group B may be applied to (6) Ratio Test Suppose
converges absolutely if L < 1, diverges if L > 1. Hint: This is useful if an involves a factorial. Watch for If the limit L is one, try another test because the Ratio Test gives no information.
|
|
Home  Infinite Series Infinite Series  Absolute and Conditional Convergence Absolute and Conditional Convergence  Summary of Series Convergence Tests Summary of Series Convergence Tests |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-07


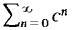

 diverges.
diverges. converges if p > 1, diverges if p ≤ 1.
converges if p > 1, diverges if p ≤ 1. converges if
converges if 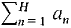 is finite,
is finite, is infinite.
is infinite. converges then
converges then  converges.
converges. diverges then
diverges then  diverges.
diverges. converges then
converges then  converges.
converges. diverges then
diverges then  diverges.
diverges. converges, then
converges, then 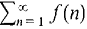 converges.
converges. diverges, then
diverges, then  diverges.
diverges. converges if the an are decreasing and approach 0. Hint: This is usually the simplest test if you see a ( - 1)n in the expression.
converges if the an are decreasing and approach 0. Hint: This is usually the simplest test if you see a ( - 1)n in the expression. converges if and only if the partial sum series
converges if and only if the partial sum series converges.
converges. converges if for all infinite H and K > H, aH+1 + ... + aK ≈ 0,
converges if for all infinite H and K > H, aH+1 + ... + aK ≈ 0, 0, diverges if limn→∞ an ≠ 0.
0, diverges if limn→∞ an ≠ 0. converges if and only if
converges if and only if  converges.
converges. converges then
converges then  converges.
converges. is a positive term series.
is a positive term series.


 in the ratio because
in the ratio because